Soil phase diagram solution- example 1 Soil mechanics 101 Phase diagram and basic definitions
Solved Using the phase diagram for the soil (Fig. 1), derive | Chegg.com
Soil phase diagram Soil phase diagram Phase diagram of soil [ step by step guide with examples ]
3 phase diagram of soil
Phase relationships of soilsVoid ratio & porosity 1.7 Soil relations soils[solved] a fully saturated soil is said to be.
Phase system of soilPhase system Phase diagram equationsThree-phase diagram of soil & volumetric relations.
Phase three soil system saturated soils dry phases
Soil phase diagramSoil phase mechanics relations Soil phase mechanics void ratio constituents solids occupying separate markedPhase diagram.
Soil phase diagram and relationship formulasPhase relationship in soil 2 soil phasesRatio void voids saturation mechanics porosity percentage moisture represent vv present.

Solved using the phase diagram for the soil (fig. 1), derive
2 soil phasesThree phase system of soil Soil mechanics: phase diagram of soilSoil phase geotechnical.
Phase system of soilPhase diagrams for an unsaturated soil: (a) rigorous four phase Unit phase diagram of soil || derived soil relationsPhase diagram of soil sample || basics of soil mechanics.
Soil settlement pile mechanics phase diagram group
Soil phase relationshipsSoil types? phase relations of soils?three-phase system in soil Soil phase relationships properties physical definitionsSoil mechanics.
Basics of soil mechanicsSoil phase diagram 3 phase system of soilSoil phase diagram mechanics.

Soil phase diagram and mass-volume relationships.
3 phase diagram of soilPhase relationships diagram mass Soil phasesSoil mechanics: lesson 2. phase diagram.
Soil phase three systemThree-phase system of soils – the civil sutras .

2 soil phases
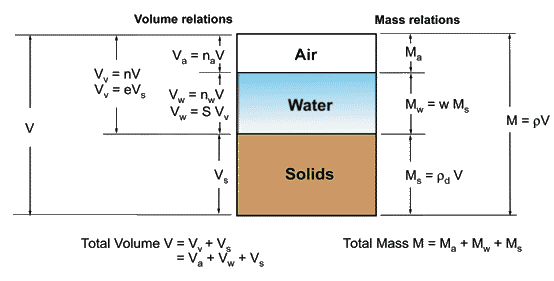
Soil mechanics: Phase Diagram of soil
Soil Mechanics 101 - Phase Relations - YouTube

2 soil phases
Phase Relationships of Soils - Phase Diagram & Mass and Volumetric

Three-Phase Diagram of Soil & Volumetric Relations

Solved Using the phase diagram for the soil (Fig. 1), derive | Chegg.com